Why Exhibit?
The ‘Auto EV India 2024’ is the place to meet a targeted clientele passionate about the EV and Automotive industry. It is the perfect event to showcase new technologies and products for EV and automotive space. South and West India is a major region for Electric Vehicle, Automotive and EV suppliers manufacturing activities.
This is a great opportunity for the industry players to meet, communicate and sell their products to a highly engaged targeted audience.
The ‘Auto EV India 2024’ is the place to network with a variety of audiences in the mobility industry. Connect with more than 250+ suppliers and source the latest technology, product and services so you can get an up-close look at cutting-edge H/EV technology and learn about the latest market innovations from across the industry.
More than 250 exhibitors and 20,000 attendees are expected to attend the show.
- A perfect place to network
- A perfect event to showcase new technology in Electric Vehicle.
- A perfect place to showcase components and technology for the EV industry
- A perfect B2B Exhibition
- The biggest testimony to the success of the second edition is the presence of more than 50 Automakers and OEMs comprising R&D and purchase team in the inaugural event. Name the top OEMs – they were present in the exhibition. The second edition would be bigger display of newest technologies from around the world and even bigger presence of the attendees.
India’s Market Potential:
Robust Demand:
- Growing working population and expanding middle class are expected to remain key demand drivers.
- By 2025, 4 million of EVs could be sold each year and 10 million by 2030. The market is expected to reach US$ 206 billion by 2030.
Export Opportunities
- India is emerging as a global hub for auto component sourcing and the industry exports over 25% of its production annually.
- Auto component exports are expected to grow and reach US$ 30 billion in FY26.
- India has a competitive advantage in auto components categories such as shafts, bearings and fasteners due to large number of players. This factor is likely to result into higher exports in coming years.
Policy Support
- 100% FDI is allowed under the automatic route for auto components sector.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes on automobile and auto components are expected to bring a capex of Rs. 74,850 crore (US$ 9.58 billion) in the next five years.
Competitive Advantage
- A cost-effective manufacturing base keeps costs lower by 10-25% relative to operations in Europe and Latin America.
- India is the second largest steel producer globally, hence has a cost advantage.
Auto Components Market Size
The Indian automobile industry is the fifth largest in the world and is expected to become the third largest by 2030. India’s auto components industry’s market share has significantly expanded, led by increasing demand for automobiles by the growing middle class and exports globally. Due to the remarkable growth in demand for Indian auto components, several Indian and international players have entered the industry.
The automobile component industry turnover stood at Rs. 4.20 lakh crore (US$ 56.5 billion) between April 2021-March 2022. In FY22, exports of auto components went up 43% to Rs. 1.41 lakh crore (US$ 19 billion). As per ACMA forecast, auto component exports from India is expected to reach US$ 30 billion by 2026. The auto component industry is projected to record US$ 200 billion in revenue by 2026. Strong international demand and resurgence in the local original equipment and aftermarket segments are predicted to help the auto component industry grow 20-23% in FY22.
EV Market Potential
CEEW-CEF study estimates a cumulative investment need of over $180 billion, Rs 12,50,000 crore, in vehicle production and charging infrastructure until 2030. EV technology evolution in India requires sizable investment in R&D and product development, both on the automobile platforms and battery/charging technology.
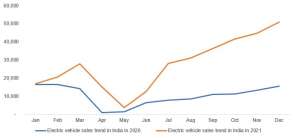
EV Market in India
As per India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA), the Indian EV industry is expected to expand at a CAGR of 36%. As population rises and demand for vehicles grows, dependence on conventional energy resources is not a sustainable option as India imports close to 80% of its crude oil requirements. NITI Aayog aims to achieve EV sales penetration of 70% for all commercial cars, 30% for private cars, 40% for buses and 80% for two and three-wheelers by 2030. This is in line with the goal to achieve net zero carbon emission by 2070. Over the last three years, 0.52 million EVs were registered in India, according to the Ministry of Heavy Industries. EVs recorded robust growth in 2021, supported by the implementation of favourable policies and programmes by the government.
Government Initiatives
The Government of India’s Automotive Mission Plan (AMP) 2006-26 has been instrumental in ensuring growth for the sector. The Indian automobile industry is expected to achieve a turnover of US$ 300 billion by 2026 by expanding at a CAGR of 15% from its current revenue of US$ 74 billion.
In November 2020, the Union Cabinet approved a PLI scheme in automobile and auto components with an approved financial outlay over a five-year period of Rs. 57,042 crore (US$ 8.1 billion). In September 2021, the Indian government issued notification regarding a PLI scheme for automobile and auto components worth Rs. 25,938 crore (US$ 3.49 billion). In February 2022, the government received an investment proposal worth Rs. 45,016 crore (US$ 6.04 billion) from 20 automotive companies under the PLI Auto scheme. This scheme is expected to create an incremental output of Rs. 2,31,500 crore (US$ 31.08 billion).
The government’s AMP 2016-26 will help the automotive industry grow and will benefit the economy in the following ways:
- The auto industry’s GDP contribution will rise to over 12%.
- Additional ~65 million direct and indirect jobs will be created.
- End-of-life policy will be implemented for old vehicles.
Key Policy Initiatives for EV sector – Growth Levers
The Government of India has always been at the forefront of framing policies related to EV adoption in the country. Few of the programmes launched by the government to increase EV adoption are shown below:
FAME India Scheme: Faster Adoption & Manufacturing of (Hybrid) Electric Vehicles (FAME) India was launched in 2015 for promoting growth and early adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles in the country. FAME-II scheme was launched in India with a budget outlay of US$ 1.3 billion (Rs. 10,000 crore) to support 1 million e-two-wheelers, 0.5 million e-three -wheelers, 55,000 e-passenger vehicles and 7,000 e-buses. The government extended the scheme until 2024, as announced in Union Budget 2022-23.
PLI Scheme: The government introduced Production Linked Incentive for Advanced Chemistry Cell Battery Storage (PLI-ACC) scheme. The scheme is expected to boost India’s battery infrastructure. As per the Union Budget, the total outlay for the scheme is US$ 2.45 billion (Rs 18,100 crore), which would be disbursed to beneficiaries over five years once the manufacturing facility is set up.
Battery Swapping Policy: A wide-spread charging infrastructure is essential for EV adoption. In this regard, on April 22, 2022, NITI Aayog released a draft battery swapping policy which will be valid until March 31, 2025. The policy will be implemented over a period of 1-2 years from the date of launch of the policy and will cover all metropolitan cities with a population greater than four million. The second phase will be implemented over 2-3 years from date of launch of the policy and will cover all UT’s and major cities with a population greater than 5,00,000.
Other Initiatives-
- Tax exemption of up to Rs.1,50,000 (US$ 1,960) under section 80EEB of income tax while purchasing an EV (2W or 4W) on loan.
- Reduction of customs duty on nickel ore (key component of lithium-ion battery) from 5% to 0%. State- wise reduction of road tax and other incentives.
- EV components such as batteries (60% of EV component revenue by fiscal 2027), drivetrains (15%), electronics (15%) and others (10%) present an opportunity for auto component makers to diversify their revenue base beyond ICE vehicles.
- According to a report by Crisil, the EV share in auto components is likely to reach 9-11 per cent by fiscal 2027 from the present 1 per cent. This at a compound annual growth rate of around 76 per cent will touch Rs 72,500 crore in fiscal 2027 from Rs 4,300 crore last fiscal. The electric vehicle segment provides both an opportunity and a challenge for the Indian component industry. On one hand, there is the challenge of many traditional IC-vehicle parts to become obsolete in the EV space, but on the other hand, new product demand could fuel growth for the nascent industry.
Growth Drivers of Indian Electric Vehicle Industry
- The burden of oil imports, rising pollution, Russia-Ukraine war escalating price inflation, as well as international commitments to combat global climate change are key factors motivating India’s policies to speed up the transition to e-mobility on one hand and growing consumer appetite on the other.
- The cost of EV batteries has been decreasing over the past decade.
- This has led to a decrease in the cost of electric vehicles as EV batteries are one of the most expensive parts of an electric vehicle.
- The prices of EV batteries are expected to fall which will greatly reduce the price of EV’s making.
- Favorable Government subsidies and policies to promote sales.
- Strict Government regulations on vehicle emission to boost growth.
Business Opportunities
The EV push in India opens a plethora of business opportunities across three key segments – mobility, infrastructure and energy. These include opportunities in EV franchising, EV OEM market, battery infrastructure, solar vehicle charging and battery swapping technology among several others. According to NITI Aayog, the complete transition to EVs requires a total investment of US$ 267 billion (Rs.19.7 lakh crore) in EVs, battery infrastructure and charging infrastructure.

